Effects of Pre-Sleep Protein Intake on Muscular Adaptations and Overnight Recovery
In the world of fitness and performance, we’re often reminded that what we do during our waking hours – the intense workouts, the carefully planned meals – shapes the foundation of our physical progress. What if there’s a hidden chapter in this narrative, a period of potential gains that occurs while we’re tucked into the realm of dreams?
Imagine a scenario where the hours you spend sleeping could be a secret weapon in your fitness arsenal. Welcome to the fascinating realm of pre-sleep protein intake and its profound effects on muscular adaptations and overnight recovery.
Diving into the intricate relationship between sleep and muscle repair, we uncover the idea where the right protein choices at the right time may unlock untapped potential.
Are you ready to explore the science behind the pillow and the plate?The Role of Protein in Muscle Recovery
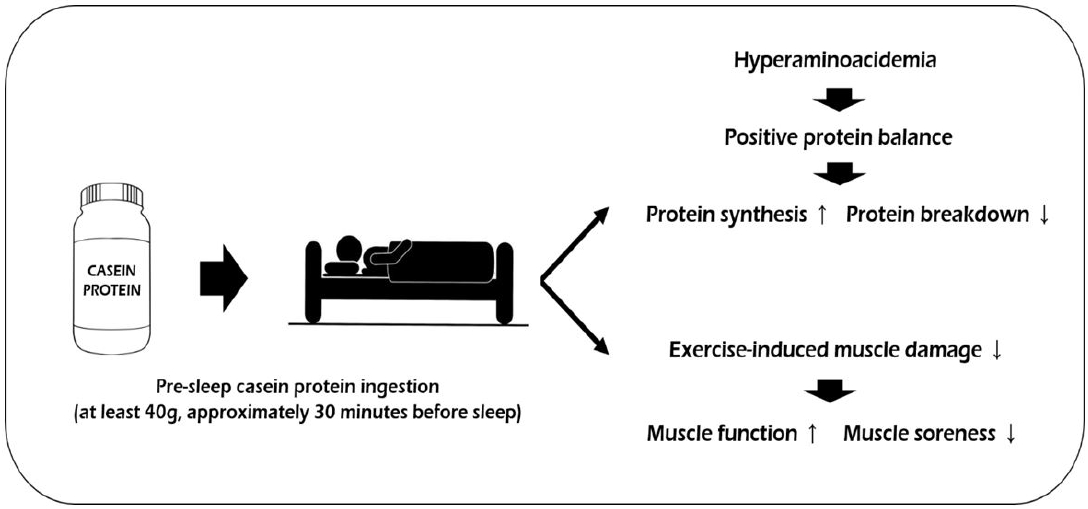
Proteins are the building blocks of muscle tissue. They contain essential amino acids, the key pieces in repairing and rebuilding muscles after an intense resistance-type workout. Consuming an adequate amount of protein is well-established as a post-exercise strategy. However, recent research suggests that the timing of protein intake, specifically before sleep, may offer additional benefits.
Effects of Pre-Sleep Protein Intake on Muscular Adaptations and Overnight Recovery
Research suggests that 30-40 grams of protein is the ideal amount before bed to significantly increase the body’s muscle protein synthesis rates, allowing a rise in muscular adaptations such as muscle strength and hypertrophy, while also facilitating muscle recovery. This protein ingestion is beneficial for an increase in muscle augmentation at a whole body level, a limb level and muscle fiber level. Although pre-sleep protein is NOT required to see these changes in adaptations and recovery, it is yet another option that is proven to be just as beneficial.
Protein Precision: Casein vs. Whey and the Overnight Advantage
While diving deeper into the research and science-based aspects, some key points I found throughout the articles include:
- Studies such as Kim, J. (2020) state that 40-48 grams of casein protein specifically can have positive effects on protein metabolism and overall exercise performance.
- In a study conducted by Snijders, T. et al (2019), they claim that pre-sleep casein protein ingestion can have the best positive chronic effects on muscle strength and hypertrophy.
- In the majority of articles I looked into, they suggested 40 grams of protein to see results during the overnight hours, as well as increase the body’s muscle protein synthesis.
Overnight Optimization: Implementing Pre-Sleep Protein for Maximum Gains
From this research, weightlifters, bodybuilders and athletes should:
Consider consuming 30-40 grams of protein before sleep.
Understand that these results require a training program in order to stimulate change.
Continue to be physically active throughout the day.
- Encourage others to follow a workout program in order to see positive results.
For more information and additional resources, click here.
About the Author
Dan Mero is a senior at Westfield State University in the Sports Medicine and Human Performance department. He will be graduating with a Bachelor’s degree in Movement Science with a Sports Medicine concentration. He plans to pursue a career in Physical Therapy. Dan can be reached at d12mero@gmail.com for additional information regarding this topic.
References
Snijders, T., Trommelen, J., Kouw, I. W., Holwerda, A. M., Verdijk, L. B., & van Loon, L. J. (2019). The impact of pre-sleep protein ingestion on the skeletal muscle adaptive response to exercise in humans: An update. Frontiers in Nutrition, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2019.00017
Trommelen, J., & VanLoon, L. J. C. (2016). Pre-Sleep Protein Ingestion to Improve the Skeletal Muscle Adaptive Response to Exercise Training. Nutrients, 8(12), 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8120763
Kim J. (2020). Pre-sleep casein protein ingestion: new paradigm in post-exercise recovery nutrition. Physical activity and nutrition, 24(2), 6–10. https://doi.org/10.20463/pan.2020.0009

Comments
Post a Comment